
This summer we celebrate the 50th Anniversary of Apollo 11. Luna 15 was an attempt to “steal the show”. This is the story
What is Luna?
Luna is to Russia as Apollo is to the United States. Luna was the title of the program to conduct interplanetary exploration by the former USSR (Union of Soviet Socialist Republics). By 1969, the former Soviet Union had launched 30 flights.
Who is in the Lead?
The Soviet Union got “out of the blocks” first when it came to space. The United States was completely caught off guard on October 4. 1957 when the Russians launched Sputnik. The 184-pound satellite became a household word in America as the Communist regime made its push for dominance in space.
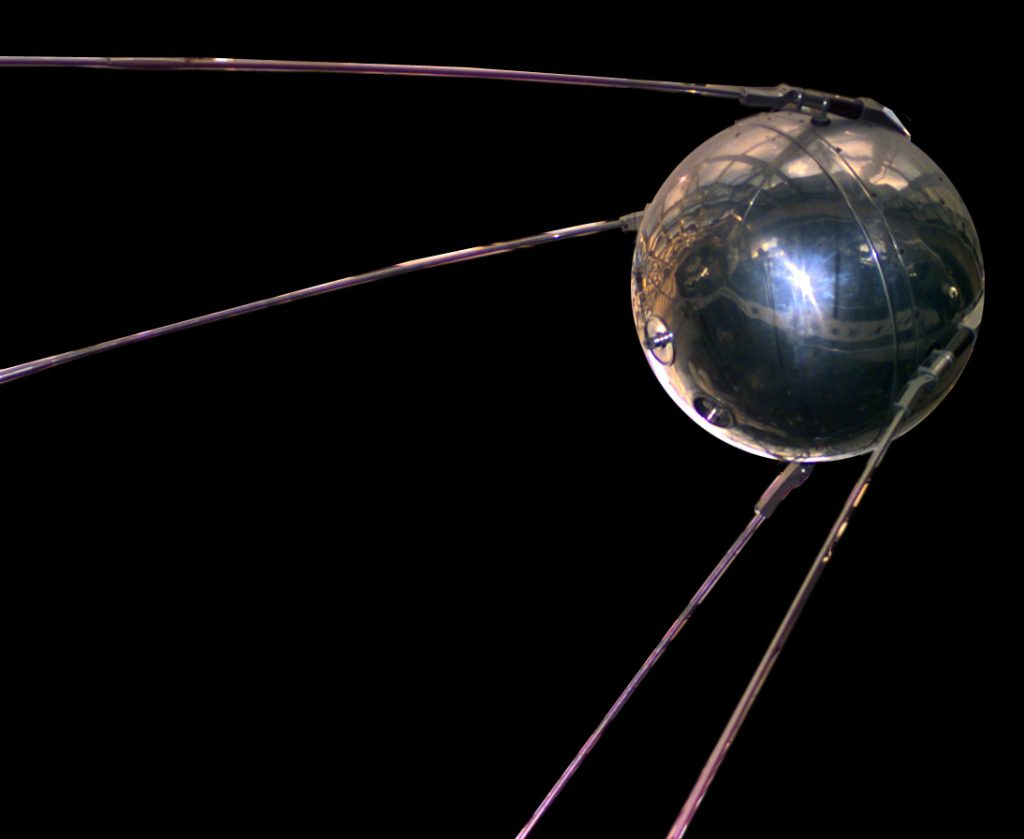

The Soviets quickly achieved a number of firsts
The first dog in space (1957)
The first rocket craft to leave earth’s orbit (1959)
The first man made object to reach the moon (1959)
The first photos of the dark side of the moon (1959)
The first man in space and orbit of the earth (1961)
First flyby of Venus (1961)
The first woman in space (1963)
First spacewalk (1965)
The first soft landing of a probe on the lunar surface (1966)
The Russians orbited a man around the earth before the United States even accomplished a sub orbital flight. However, by 1967 the United States caught and began to pass the Russians in the race to the moon.
Desperate Times
Desperate times call for desperate measures. By early 1969, the Soviets realized that they were going to be beaten to the moon. What does one do when they feel defeated? Often one attempts to rob the winner of some of their glory. The Soviets decided to try to steal some thunder from the Apollo 11 mission.
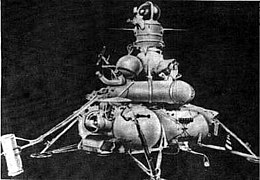
Luna-15 was designed to fly to the moon via remote control. The spacecraft was to enter lunar orbit, descend to the lunar surface, collect rock samples, blast off and return to the earth. If the craft accomplished the mission, the USSR could claim to be the first nation to bring back lunar samples. In some way, it would preserve the national dignity of the USSR.
Luna 15

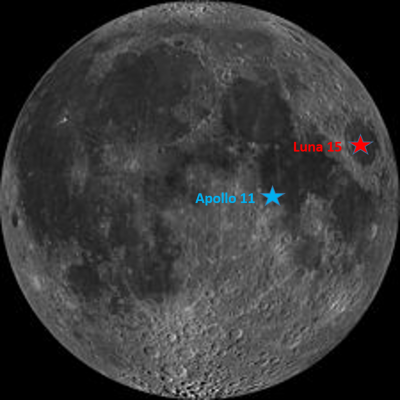
Luna 15 blasted off on July 13, three days before Apollo 11. It was literally a race to the lunar surface. American intelligence and Russian announcements alerted the United States to the flight. Frank Borman (of Apollo 8) was sent to the Soviet Union to ensure that no interference between the missions would occur. To their credit, the Soviets shared flight specifics to calm American fears of collisions. Still the Luna mission was cloaked in secrecy.
Luna 15 entered lunar orbit on July 17, 1969. Inexplicably it remained in orbit for four days, completing 52 orbits of the moon. Why did the spacecraft delay for four days? We have only speculation, but it seems that the Soviets were working on problems with the spacecraft and searching for suitable landing sites.
Meanwhile, Apollo 11 arrived in lunar orbit on July 19. Apollo 8 had surveyed possible landing sites the previous Christmas of 1968, so there was little investigative work to be done for a landing target. On July 20, Armstrong and Aldrin climbed into the Lunar Module (The Eagle) and began to descend to the moon, meanwhile Luna-15 remained in lunar orbit.
Luna 15 finally began what was a planned five-minute descent to the lunar surface on July 21. Armstrong and Aldrin had already landed, walked on the moon, and returned to the Eagle Lunar Module. For four minutes, Luna 15 communicated as planned to the Russian home base. Then, silence. Nothing.
It is theorized that Luna 15 crashed onto the side of a mountain almost two miles above the lunar surface. The mission and the Russians last hope of stealing some thunder were dashed.
The Play by Play
While all this occurred, British scientists were monitoring both Apollo and Luna radio transmissions. For four decades, these recording remained classified. They were release on the 40th anniversary of Apollo 11 in July 2009. See this story to read more details and listen to the audio files.

See also: NASA Summary
